The OWASP Top 10 for Agentic Applications: A Milestone for the Future of AI Security

The OWASP GenAI Security Project has officially released its Top 10 for Agentic Applications, the first industry-standard framework focused on the operational risks created by autonomous and semi-autonomous AI systems. AI has evolved in a way that directly changes how enterprises need to think about security. We started with machine learning systems designed to classify and predict. Large language models added reasoning and natural language interaction, which expanded AI’s usefulness but still kept it mostly confined to generating output.
We are now in the agentic era; agents plan, reason, access data, invoke tools, and take actions that materially impact enterprise systems, users, workflows, and risk posture. This is how AI is being operationalized inside organizations today, and it is where the security impact is most critical. This OWASP project marks a turning point in how the industry frames AI risk and helps security teams more clearly recognize and categorize the operational risks introduced by agentic systems.
We’re grateful for the opportunity to contribute to this important community effort. Zenity co-founder and CTO Michael Bargury participated as a distinguished reviewer, and in my role as Director of AI Security and Policy Advocacy, served as a core contributor and entry lead. Our involvement alongside the great panel of experts in AI security is built towards helping ensure the frameworks that security teams put into use reflect the kinds of risks defenders are already encountering as agents begin taking action inside business systems.
OWASP recognizing this distinction is a huge milestone: it’s the formal acknowledgment that AI Agent Security is its own category. For Zenity, it’s also a moment of confirmation, this is the problem space we’ve been out in front of for years, and the OWASP Top 10 for AI Agents now gives the entire industry a common language for risks our customers have already been managing with Zenity in the loop.
Why the OWASP AI Agent Top 10 Matters Now
As enterprises adopt agents from both leadership mandates for competitive edges and from rank-and-file experimentation, agents are quickly becoming the primary way that AI is used in real business environments, with innovative companies like SoftBank and Salesforce previously stating and now marching towards their ambitious goals to have 1 billion agents in production in short order. That shift, from static output to dynamic execution, changes the security landscape completely.
Traditional controls built for model-centric risk (prompt filtering, DLP, retrieval hardening) don’t cover the parts of AI that actually introduce operational risk: planning, tool invocation, memory, delegation, reasoning chains, inter-agent communication, and real-world actions. Most AI security tools only protect one layer of the stack, leaving gaps in terms of understanding what agents do, how they do it, and why they behave as they do.
The OWASP AI Agent Top 10 arrives at a moment when organizations need clear terminology and structure to describe these emerging and critical risks. By articulating distinct categories of agent-related threats, it provides a foundation that security leaders and practitioners can use to assess where operational vulnerabilities exist and how to begin addressing them.
Zenity’s Perspective on the OWASP AI Agent Top 10
Below is Zenity’s POV on each of the OWASP Top 10 risks for AI Agents, and why each risk underscores the need for agent-centric security measures.
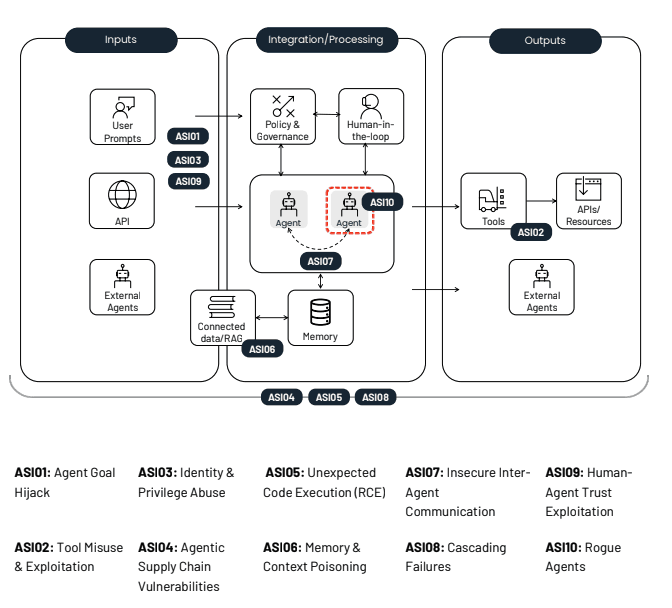
ASI01 — Agent Goal Hijack
This was the section that I served as the entry lead for, and it's near and dear to my heart. Prompt injection is more than just malicious inputs that manipulate outputs, the underlying goal for attackers is to redirect behavior. Because agents cannot reliably distinguish instructions from context, attackers can covertly change goals, rewrite plans, or shift intent.
Mitigating Agent Goal Hijack risk: Goal integrity is foundational. Runtime intent analysis and guardrails are required to detect and block when an agent is being persuaded to do something outside its authorized scope.
ASI02 — Tool Misuse & Exploitation
Agents can, and often do misuse legitimate tools for harmful actions when instructions are misinterpreted, misaligned, or maliciously influenced.
Mitigating Tool Misuse & Exploitation risk: Agents must be governed not only by what they can access, but how they use those capabilities. Our platform applies inline policy enforcement that governs tool invocation and prevents dangerous sequences before they execute.
ASI03 — Identity & Privilege Abuse
Agents often operate with inherited tokens, secrets, cached identities, or overly broad access scopes. Attackers can then exploit these permissions to move laterally and vertically throughout the network, and/or trick a high-privilege agent into acting for them.
Mitigating Identity & Privilege risk: Enforce least privilege, define explicit identity boundaries, and prevent unauthorized delegation chains. Agent identities must be treated like privileged service accounts, meaning continuous monitoring and enforcement throughout their lifecycle.
ASI04 — Agentic Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Every component an agent relies on, whether it be models, tools, MCP servers, or prompt templates, all are part of a live supply chain. As we’ve seen, a single compromised dependency can cascade into agent compromise.
Mitigating Agentic Supply Chain Vulnerabilities risk: Enterprises need full observability into every agent, tool, plugin, and dependency across cloud, SaaS, and endpoints. We're able to unify these signals and dependencies into one control plane for risk assessment and action with our Attack Graph.
ASI05 — Unexpected Code Execution (RCE)
Agents generate and execute code regularly, making it trivial for attackers to turn natural language into RCE payloads that can impact agents without even needing an end user to click anything.
Mitigating Unexpected Code Execution risk: As we showed at BlackHat 2024, agent execution must be sandboxed, validated, and monitored. Behavioral detection is required, because static filters fail against dynamic code generation.
ASI06 — Memory & Context Poisoning
Long-term memory, a core component of agentic usefulness, when impacted can turn prompt injection attacks from a momentary exploit into a persistent, hard-to-detect compromise.
Mitigating Memory & Context Poisoning risk: Analyze decision paths, memory writes, and context usage to detect poisoning attempts and prevent corrupted memory from influencing behavior in real time.
ASI07 — Insecure Inter-Agent Communication
When agents are connected with each other (multi-agents), spoofed messages, manipulated coordination, or cross-agent data leakage can lead to cascading harm.
Mitigating Insecure Inter-Agent Communication risk: Authentication, validation, and semantic checks are mandatory. Zenity enforces governed communication flows across multi-agent environments.
ASI08 — Cascading Failures
Because agents plan, delegate, and act autonomously, small deviations like a single hallucination, poisoned memory item or compromised tool, can trigger large operational failures before humans notice.
Mitigating Cascading Failures risk: Implement step-level insight and real-time defense to stop high-risk activity before it triggers downstream effects.
ASI09 — Human-Agent Trust Exploitation
Humans over-trust agents, not just in keeping their secrets safe, but also in inherently trusting the answers agents give them. Attackers in turn exploit this by manipulating agents to socially engineer users.
Mitigating Human-Agent Trust Exploitation risk: User-facing agent actions must be governed, verified, and monitored—especially actions that involve financial transactions, approvals, or data exposure.
ASI10 — Rogue Agents
Agents can quickly become misaligned, compromised, or intentionally malicious, deviating from their authorized goals while still appearing superficially compliant. Once its behavior drifts, it may exfiltrate data, hijack workflows, self-replicate, or coordinate with other agents in harmful ways.
Mitigating Rogue Agents risk: Agents require continuous behavioral oversight with the ability to block malicious actions inline. Zenity’s intent-based engine intervenes at the moment of action to ensure agents behave within approved boundaries.
The Case for Agent-Centric AI Security
As enterprises continue to deploy agents in their environments across SaaS, the cloud, the endpoint, and the browser, the primary area of risk shifts from the underlying model to the decisions, permissions, and behaviors of the agent itself. Security teams need to understand and control what agents do, not just what models generate.
OWASP’s Top 10 for Agentic Apps makes clear that effective AI security must account for how agents behave in production environments, what they can access, and how they execute tasks. As adoption scales, governing these operational behaviors becomes essential for maintaining safety and resilience. Security teams need:
- Visibility into every agent, its actions, identity, memory, and tools
- Secure-by-design governance across configurations, permissions, and workflows
- Real-time defense that blocks risky agent actions before they execute
This is exactly the architecture Zenity built from day one and we are hyper-focused on giving organizations control over what AI does. AI Agents are the operational unit of AI, and securing them is the foundation of AI Security.
Our Commitment to the Community
We are proud to support and work with OWASP, sharing the mission to bring clarity, rigor, and standards to the rapidly developing world of agentic AI. This effort reflects our broader commitment to supporting the community of defenders that are standing up and facing the inherent threats that come with AI agents. Standards and shared frameworks play an important role in helping organizations navigate emerging risks, and we will continue contributing research, testing, and field insight to strengthen the community’s understanding of how agents behave in practice.
As adoption accelerates, security teams will need clearer guidance, better data, and practical ways to assess and govern agents. We remain focused on advancing this work with the community and on helping organizations build the foundations required for safe and resilient use of agentic AI.The OWASP Top 10 for AI Agents marks yet another landmark for the security transformation happening across the AI landscape. And Zenity is here to lead it. If you'd like to learn more about how we're helping our customers implement security controls to mitigate the risks outlined in the newest OWASP Top 10, get in touch!
All ArticlesRelated blog posts

Inside the Agent Stack: Securing Agents in Amazon Bedrock AgentCore
In the first installment of our Inside the Agent Stack series, we examined the design and security posture of agents...

Inside the Agent Stack: Securing Azure AI Foundry-Built Agents
This blog kicks off our new series, Inside the Agent Stack, where we take you behind the scenes of today’s most...

When “Secure by Design” Isn’t Enough: A Blind Spot in Power Platform Security Access Controls
Security Groups play a pivotal role in tenant governance across platforms like Entra, Power Platform, and SharePoint....
Secure Your Agents
We’d love to chat with you about how your team can secure and govern AI Agents everywhere.
Get a Demo